 In this video we discuss how to calculate the cumulative frequency and construct a cumulative frequency distribution table. We also define what is cumulative frequency.
In this video we discuss how to calculate the cumulative frequency and construct a cumulative frequency distribution table. We also define what is cumulative frequency. Transcript/notes
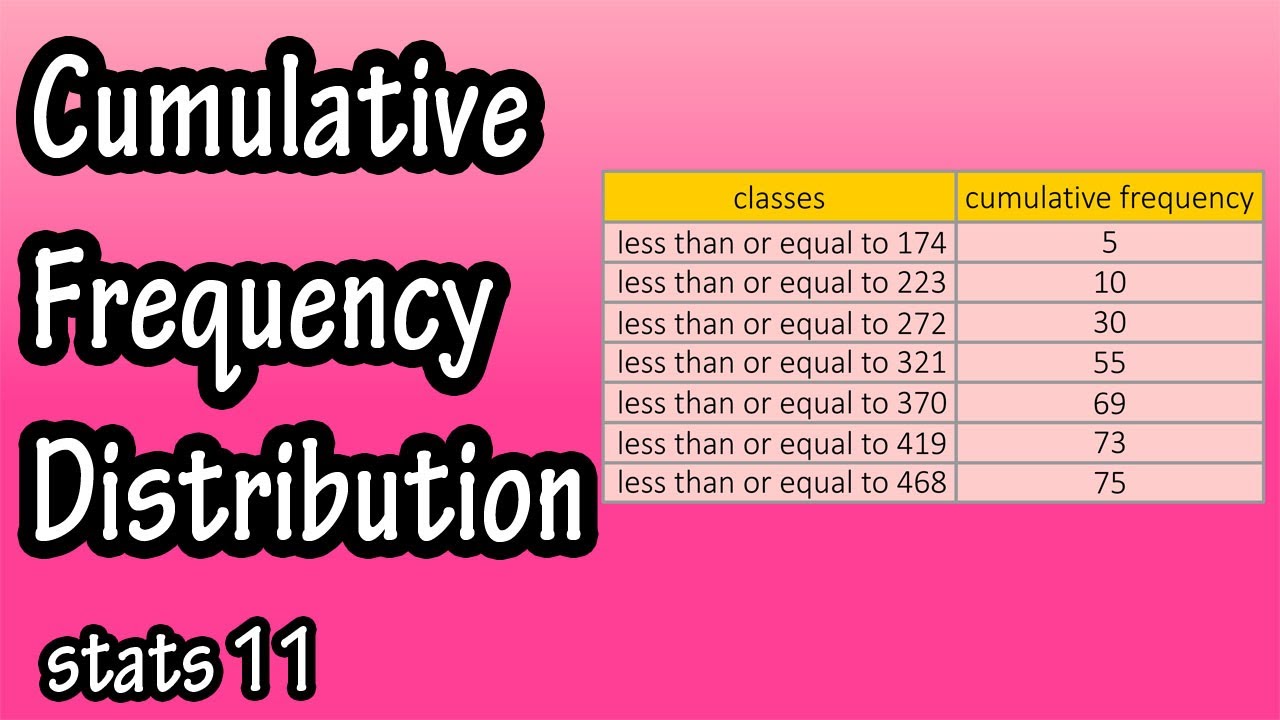
Cumulative frequency distribution
In a past video we discussed what a frequency distribution is. Real quick, you have a data set, you break the data down into classes or intervals, column 1, you tally up how many data points are in each class, column 2, and you write that number down, which is the frequency, column 3.
A cumulative frequency distribution shows the number of data values less than or equal to the upper class limit of a given class. The upper class limit for the first class is 174, so, we want to find all of the data values in the data set that are less than or equal to 174. Since we already have a tally, we know that there are 5 data points that are less than this number. You could also just look at the frequency column to get this number.
Next we look at the upper limit of the second class and see that number is 223. So, we want to find all of the data values in the data set that are less than or equal to 223. We again look at either the tally or frequency and see that there are 5 data points in class 1 and 5 data points in class 2, so the total number of data points that are less than or equal to 223 are 10.
And you would continue this process for the other 5 classes. Once you have finished, the cumulative frequency number you have in the last class should be equal to the total number of data points in the data set, in this case 75.
Basically what we are doing is adding up all of the data points that lie under a specific value, in this case an upper class limit. This allows you to organize the data a bit more in depth, and allows you to look at the data in a different way, to get another perspective on the data.


0 Comments